Now that your 3D printer has been upgraded to support flexible filaments like PETG, you can get started. PETG filament's strength and resistance to chemicals present some fascinating opportunities. However, it's crucial to comprehend how PETG varies from PLA and how to achieve the greatest outcomes before you begin printing. PETG can be more difficult to print on, but if you use these pointers, you'll soon be producing prints that look professional. The secret is to fine-tune your printer, select the appropriate settings, and give yourself enough time to make mistakes. PETG might need more perseverance, but the benefits are worthwhile. Continue reading to master the art of printing with this multipurpose filament.
What Is PETG Filament?
PETG filament, derived from polyethylene terephthalate glycol, is a widely used material for 3D printing. It is a flexible, long-lasting polymer that combines the qualities of PET (plastic water bottles) and PBT.
PETG is a fantastic material for beginners because it is more forgiving than PLA and easier to print with. It causes less warping and adheres to build plates nicely without the need for a hot bed. With PETG, stringing and oozing are likewise less common.
PETG components are chemically stable, watertight, and resistant to impact after printing. They won't distort in temperatures as high as 70–80°C. Because PETG has a small amount of elasticity, printed objects won't break easily under pressure. Plus, it's totally recyclable.
The primary drawbacks of PETG are its difficulty in producing smooth surfaces and delicate details. Unlike PLA, it is not biodegradable either. For better aesthetics, PETG components could need additional post-processing.
In terms of printability and usefulness, PETG lies between PLA and ABS in a sweet spot for most manufacturers and hobbyists. PETG is an excellent material to test if you're looking for robust 3D printed objects that don't require a hot build chamber.
Key Properties and Benefits of PETG Filament
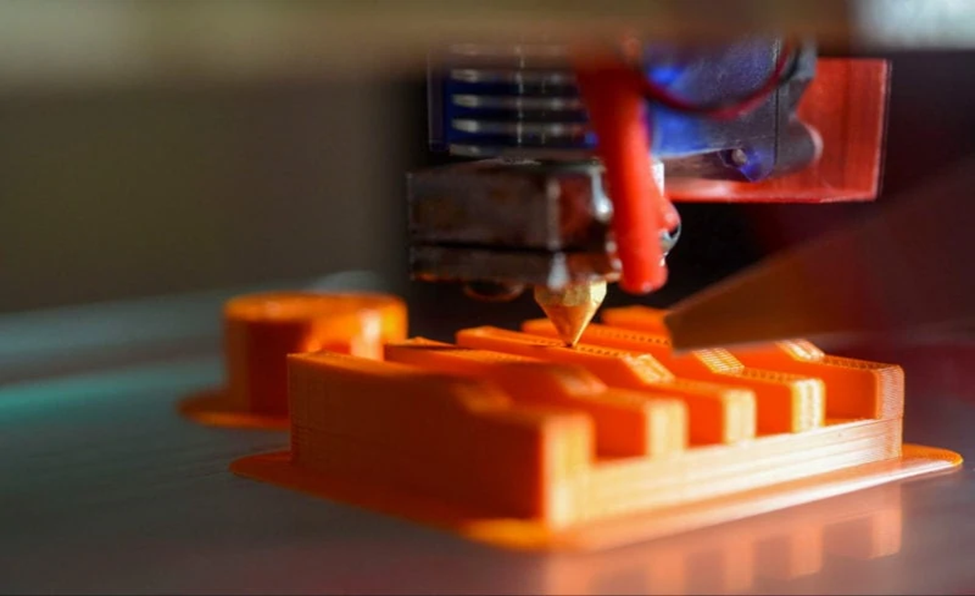
PETG filament works well for 3D printing because of a few beneficial characteristics. It is resilient to impact and long-lasting. Drops and impacts that would shatter ABS or PLA prints are not a problem for PETG. While it's not unbreakable, it breaks less frequently.
Second, PETG filament can withstand chemicals. It is resistant to chemicals, solvents, and oils that could harm other polymers. Because of this, it works well for containers, mechanical parts, and other uses where chemical resistance is beneficial.
PETG filament has a few advantageous properties that make it ideal for 3D printing.
It is long-lasting and impact-resistant. PETG is not affected by drops or impacts that would break ABS or PLA prints. It's not indestructible, but it breaks less often.
Third, the heat deflection temperature of PETG is high. It can tolerate temperatures up to 70–80°C, which is 10–30°C greater than PLA, before starting to soften. In light of this, PETG prints are able to withstand hot summer days in cars and other high-temperature settings where PLA would malfunction.
Lastly, PETG filament adheres to print beds quite nicely, however when finished, pieces simply peel off. The print bed doesn't require any extra care, and after the parts cool, releasing them is simple. PETG is particularly user-friendly as a result.
Settings and Tips
Use a hot print bed (70–80°C) while printing PETG. Typical nozzle temperatures range from 230 to 250°C. Print at a slower speed (30–60 mm/s) than PLA. Pick a layer height of no more than 0.2 mm. For overhangs, activate cooling, and refrain from printing PETG pieces that are entirely separated from the print bed.
PETG filament can create robust, long-lasting parts with a glossy, appealing appearance when used with the proper settings. Try it out on your upcoming useful print!
PETG Filament Print Settings - Temperature, Speed, Bed Adhesion
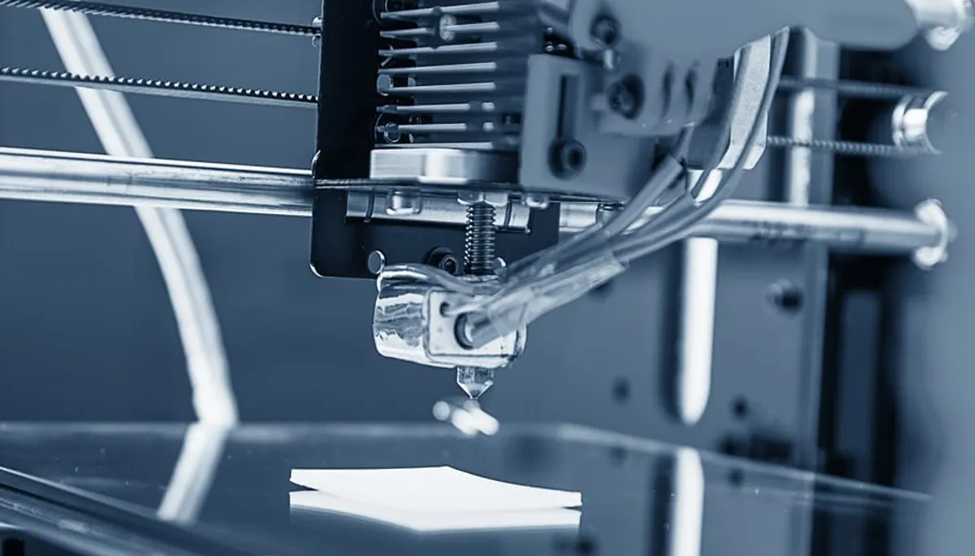
The secret to successful PETG filament printing is fine-tuning the parameters. PETG can be a little picky, but with some practice, you'll quickly produce flawless prints.
Temperature
Print with PETG filament at 230–250°C for optimal results. If necessary, start at the lower end of the range, or about 235°C, and gradually raise the temperature. A temperature that is too low will not supply the PETG enough heat to melt it adequately, which can cause blockages and poor adhesion between layers. Your prints may thread, ooze, or lose detail if the temperature is too high.
Speed
The race is won by PETG with a steady pace. At 30-60 mm/s, print for optimal quality. Reduced rates (around 40–50 mm/s) offer the hotend more time to melt the PETG, improving layer adhesion and strengthening the print as a whole. Faster speeds frequently result in blobs, stringing, and poor layer adhesion. Launch at 40–45 mm/s and modify as necessary.
Bed Adhesion
PETG adheres to building surfaces very well—sometimes too well, thus it's critical to have a suitable bed adhesion. Apply a layer of PETG slurry, hairspray, or glue stick to glass or bare metal beds to form a release layer. By doing this, the PETG won't fuse with the bed. You can now print after applying two to three layers, letting each one dry for a few seconds, and leveling your bed.
You can print excellent PETG parts quickly if you have the ideal temperature, speed, and bed adhesion parameters. Because of the nature of PETG filament, little stringing and oozing may still happen even with optimal settings. A clean finish can be achieved by quickly passing a heat gun over the extra material after trimming it with flush cutters. Enjoy your printing!
PETG Filament Print Tips and Tricks
Here are some pointers to assist you attain excellent prints after your PETG filament is loaded and ready to print:
Printing Temperature
Higher temperatures are ideal for PETG filament printing, usually between 230 and 250 C. Make adjustments in five degree increments, starting at the lower end of the range. Higher temperatures will result in a glossier finish and improved layer adherence. If it's too low, you'll have weak layer bonding and stringing
Retraction Settings
With PETG, stringing is prevalent, thus it's important to fine-tune your retraction settings. Raise your retraction speed to 25–30 mm/s and retraction distance to 6–8 mm. This will lessen stringing and oozing. Changes might be necessary depending on the printer and PETG brand you are using. Adjust the settings to reduce the amount of stringing.
Slow Down!
You will get better results if you slow down your print speed because PETG flows more than PLA. For infill and perimeters, aim for 30–50 mm/s; for minor details, try 10–30 mm/s. reduced stringing and increased strength are achieved by slower rates, which give the filament more time to adhere to the layer beneath.
Part Cooling
PETG hardens and bonds layers without the need for active cooling, in contrast to PLA. In actuality, poor layer adhesion with PETG can result from excessive component cooling. Either fully shut off or adjust your part cooling fan to a maximum of 30%. The portion will adhere to the layers more strongly the hotter it remains.
Bed Adhesion
PETG adheres firmly to a variety of print bed surfaces, including glass, and blue painter's tape. For the optimum adhesion, apply an adhesive on the bed, such as PETG slurry, glue sticks, or hairspray. Selecting the right material for your bed is important because PETG can be challenging to get off of walls. An enclosure that keeps the surrounding temperature higher will also aid in bed adhesion.
You can become more comfortable printing PETG filament by paying attention to these pointers. Adjust a few adjustments here and there to suit your unique configuration. You'll quickly be printing robust, excellent parts with a little experimentation!
Best Uses for PETG Filament - When to Choose PETG Over other Materials

PETG filament is a fantastic option for a variety of helpful and realistic prints. Because of its strength and adaptability, it is ideal for use in situations where other materials would not hold up. These are a few of the top applications for PETG coil.
Containers and Storage
PETG is perfect for jars, storage bins, and containers since it is water- and food-resistant. Make prints for vases, mugs, pitchers, or any other container for liquids. These things are resistant to impact, so they won't break or crack easily.
Mechanical Parts
PETG is an excellent choice if you require a robust, flexible material for mechanical parts like sliders, gears, or hinges. It can bend without breaking and has good layer adhesion and compressive strength.
Prototyping
PETG is an excellent filament for creating models and prototyping. It prints easily, sands and machines easily, and can be coated for a glossy appearance. Make use of it to build prototypes, mockups, and models before spending money on tools for the finished products.
Signs and Displays
Use PETG to create personalized nameplates, signage, and displays. Its weather resilience and longevity make it suitable for outdoor use, and adding backlighting with acrylic sheet inserts is a simple process. PETG adheres effectively to solvent cements, hot glue, and epoxy.
Children's Toys
PETG is ideal for toys and other child-related products since it is robust, safe, and impact-resistant. PETG filament can be used to print puzzle pieces, building blocks, toy cars, dolls, or action figures because it is strong against chemicals and won't shatter easily under impact.
In conclusion, PETG filament is perfect for robust and useful prints where chemical resistance, flexibility, and impact resistance are crucial. PETG is the ideal material to use when you need something more durable than PLA but more manageable to print than ABS.
Conclusion
These are the fundamentals needed to begin printing with PETG filament like a pro. With a little practice, you'll be producing prints of excellent quality in no time. Remember to perform some test prints in order to fine-tune those parameters for your particular printer and filament. Once you get the hang of it, PETG may yield some really polished and long-lasting effects. Your abilities to produce will astound your friends and family. Who knows, maybe you'll become so proficient at it that you decide to start selling prints on the internet or at nearby craft fairs. There are countless options. Now go forth and begin printing! You can do this.






Leave a Reply